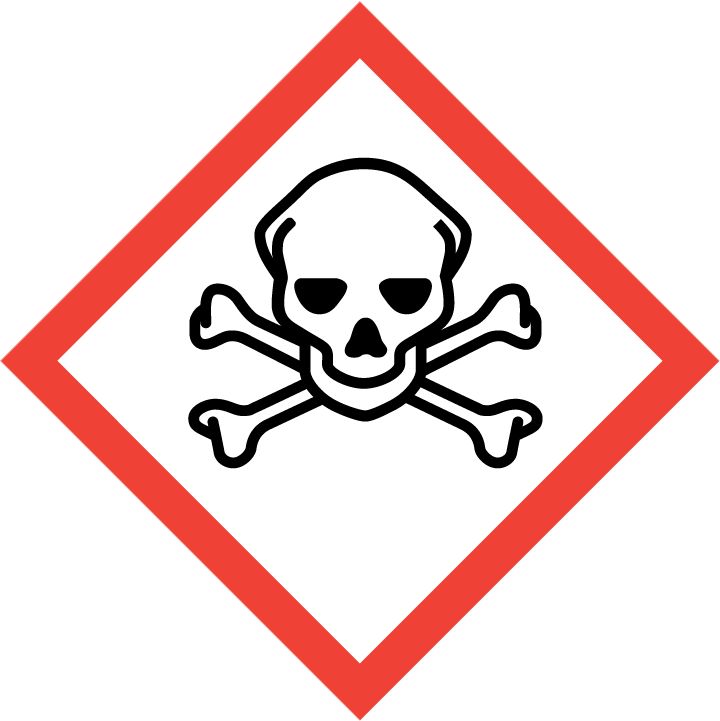
3-Chloro-5-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, also known by its chemical formula C7H4ClFO2, plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis processes due to its unique properties and reactivity. This versatile compound is commonly employed as a building block in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals.1. Synthesis of pharmaceuticals: 3-Chloro-5-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde serves as a key intermediate in the production of different pharmaceutical compounds. Its hydroxy and aldehyde functional groups make it a valuable precursor in the synthesis of diverse drug molecules, including anti-inflammatory agents, antibiotics, and anti-cancer drugs. By incorporating this compound into the chemical structure of pharmaceuticals, researchers can fine-tune the properties of the final products for enhanced efficacy and reduced side effects.2. Agrochemical applications: In the field of agrochemistry, 3-Chloro-5-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde finds utility in the development of pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides. By harnessing its reactive properties, scientists can modify the molecular structure of this compound to create active ingredients that target specific pests or diseases affecting crops. The resulting agrochemical formulations help enhance crop yield, improve plant health, and minimize environmental impact.3. Fine chemical synthesis: Furthermore, 3-Chloro-5-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde contributes to the synthesis of various fine chemicals used in industries such as fragrance, flavor, and cosmetics. Its distinct chemical structure and functional groups enable researchers to design novel molecules with specific aromatic profiles and chemical properties. By incorporating this compound into the production of fine chemicals, manufacturers can create high-quality products that cater to diverse consumer preferences.Overall, 3-Chloro-5-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde serves as a fundamental building block in chemical synthesis, facilitating the creation of a wide range of valuable compounds with applications in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals. Its versatility and reactivity make it an essential tool for chemists and researchers seeking to develop innovative solutions for various industries.